optical memory smart cards Optical cards find use in many portable data storage applications with the largest usage being secure personal identification (ID) cards — for example, the US Permanent Resident Card ("green card") and the Italian national ID card.
Resident and non-resident Pakistanis can avail Visa debit cards against their Roshan Digital Foreign Currency Value account (FCVA) and Foreign Currency (FCY) accounts. These cards are designed to complement your .Are you ready to bust three myths about contactless cards? So let's jump right in. Three myths about the dangers of contactless cards. See more
0 · What Is a Smart Card? Definition and Guide
1 · Smart Card Overview
2 · Smart Card Access Control Systems
3 · Smart Card
4 · GAO
5 · About Smart Cards : Frequently Asked Questions
Updated by PA 1y ago. You will need to bring along your new PAssion Silver Concession Card and original NRIC, and visit any TransitLink Ticket Office or Concession Card Replacement Office to activate your card. Topics: PAssion Card Silver Concession.
Optical Memory Cards. Optical memory cards look like a card with a piece of a CD glued on top - which is basically what they are. Optical memory cards can store up to 4 MB of data. But once .Optical Memory Cards. Optical memory cards look like a card with a piece of a CD glued on top - which is basically what they are. Optical memory cards can store up to 4 MB of data. But once written, the data cannot be changed or removed.
A smart card is a device that includes an embedded integrated circuit that can be either a secure microcontroller or equivalent intelligence with internal memory or a memory chip alone. The card connects to a reader with direct physical contact or with a . Hybrid Smart Cards: Have a magnetic stripe in addition to the chip. Provide fallback option for legacy magnetic stripe readers. Optical Memory Cards: Use optical storage media instead of magnetic stripes or chips. Higher storage capacities. RFID Cards: Embedding a paper or plastic card with a passive RFID tag. This chapter provides a first introduction to a wide range of smart cards and tokens, considering the various types, capabilities, popular applications and the practicality of their development and deployment, covered in detail within .
Optical cards find use in many portable data storage applications with the largest usage being secure personal identification (ID) cards — for example, the US Permanent Resident Card ("green card") and the Italian national ID card. Due to its microcomputer and programmable memory, a smart card can cater for the specific needs of the environment it is used in. Smart cards allow the secure handling and storage of sensitive data such as user privileges and cryptographic keys as well as the execution of cryptographic algorithms. Optical cards use some form of laser to read and write to the card. The U.S. Gov issued “Green Card” for example has optical storage capability. Simply put it pretty much acts like a DVD on a strip and requires highly proprietary equipment to access data stored on such card.
The term “smart card” is loosely used to describe any card that is capable of relating information to a particular application such as magnetic stripe cards, optical cards, memory cards, and microprocessor cards.Optical Card: An optical card uses some form of laser to read and write to the card. Intended for uses similar to those of a magnetic-stripe card, an optical card has much higher capacity. This type of card is most frequently used for secure personal ID .Smart cards provide the secure, convenient and cost-effective ID technology that stores the enrolled biometric template and compares it to the “live” biometric template.
Optical Memory Cards. Optical memory cards look like a card with a piece of a CD glued on top - which is basically what they are. Optical memory cards can store up to 4 MB of data. But once written, the data cannot be changed or removed.

What Is a Smart Card? Definition and Guide
A smart card is a device that includes an embedded integrated circuit that can be either a secure microcontroller or equivalent intelligence with internal memory or a memory chip alone. The card connects to a reader with direct physical contact or with a . Hybrid Smart Cards: Have a magnetic stripe in addition to the chip. Provide fallback option for legacy magnetic stripe readers. Optical Memory Cards: Use optical storage media instead of magnetic stripes or chips. Higher storage capacities. RFID Cards: Embedding a paper or plastic card with a passive RFID tag. This chapter provides a first introduction to a wide range of smart cards and tokens, considering the various types, capabilities, popular applications and the practicality of their development and deployment, covered in detail within . Optical cards find use in many portable data storage applications with the largest usage being secure personal identification (ID) cards — for example, the US Permanent Resident Card ("green card") and the Italian national ID card.
Due to its microcomputer and programmable memory, a smart card can cater for the specific needs of the environment it is used in. Smart cards allow the secure handling and storage of sensitive data such as user privileges and cryptographic keys as well as the execution of cryptographic algorithms. Optical cards use some form of laser to read and write to the card. The U.S. Gov issued “Green Card” for example has optical storage capability. Simply put it pretty much acts like a DVD on a strip and requires highly proprietary equipment to access data stored on such card.
The term “smart card” is loosely used to describe any card that is capable of relating information to a particular application such as magnetic stripe cards, optical cards, memory cards, and microprocessor cards.
Optical Card: An optical card uses some form of laser to read and write to the card. Intended for uses similar to those of a magnetic-stripe card, an optical card has much higher capacity. This type of card is most frequently used for secure personal ID .
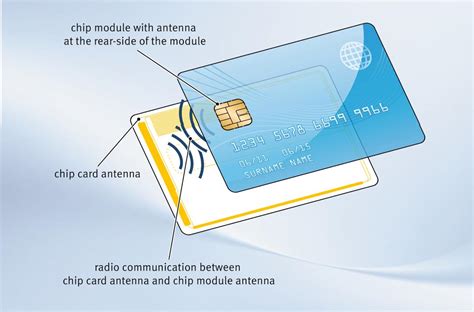
Smart Card Overview
$35.96
optical memory smart cards|GAO