rfid id card contactless reader field Contactless smart card readers use Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology or Near-Field Communication (NFC) to communicate with a card. The card needs to be in close proximity to the reader, but no physical contact is required. $7.11
0 · rfid handbook pdf
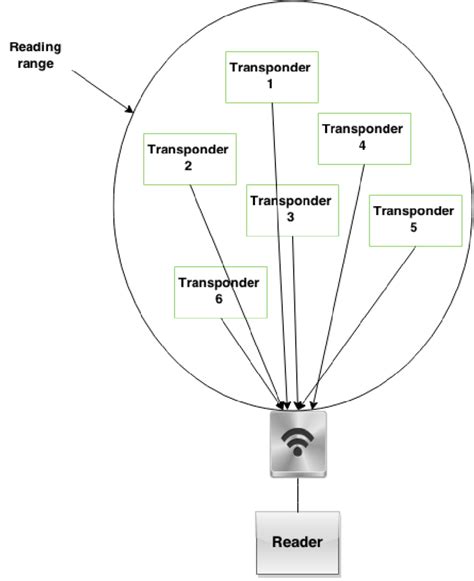
1 · multi access rfid procedures
This shift from physical wallets to a device-first approach will continue to accelerate in the coming years, with consumer usage of digital wallets already diversifying to store transportation tickets (89% of respondents), event .
Contactless smart card readers use Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology or Near-Field Communication (NFC) to communicate with a card. The card needs to be in close proximity to the .
RFID contactless smart cards use radio frequency identification technology to communicate . Contactless smart card readers use Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology or Near-Field Communication (NFC) to communicate with a card. The card needs to be in close proximity to the reader, but no physical contact is required.RFID contactless smart cards use radio frequency identification technology to communicate with a reader at the point of sale (POS). Inside each card is a small RFID chip that stores and transmits data through radio waves when placed near an RFID-enabled reader. Unlike traditional credit or debit cards that require physical contact with a POS .
Fundamentals and Applications in Contactless Smart Cards, Radio Frequency Identification and Near-Field Communication, Third Edition / Klaus Finkenzeller ; translated by Dorte M¨ ¨uller. – 3rd ed. Contactless Smart Card Readers. Contrary to their contact counterparts, contactless smart card readers do not require a physical connection with the card. Instead, they use radio-frequency identification (RFID) technology or Near-Field Communication (NFC) to communicate with a smart card.High-Frequency Smart Card Readers. Contactless 13.56 MHz smart cards (e.g. ISO-14443A/B, ISO-15693). Reader options available for reading the Card Serial Number (CSN), iClass or SEOS, or secure memory area (e.g. MIFARE DESFire, Classic, Plus or Ultralight LEGIC). Learn more.Automotive: Implementing electronic toll collection, vehicle identification, and anti-theft systems. Payment Systems: Enabling contactless payments with credit and debit cards and mobile devices. Conclusion: RFID, NFC, and contactless smart cards offer transformative potential across various sectors. By understanding the
contactless smart cards are getting smarter while RFID tags are getting dumber. Typically, a contactless smart card that targets banking, transport, and ID applications will operate at short range (less than 4 inches or 10 centimeters).The WAVE ID Solo delivers plug and play functionality with proximity and contactless smart cards and integrates with all leading operating systems, applications and embedded controllers.Contactless smart card is smart card that can exchange data without physical contact. They communicate by using radio waves, contain embedded antennas and chips, and use RFID (radio frequency identification) technology to achieve data transmission.
This is the third revised edition of the established and trusted RFID Handbook; the most comprehensive introduction to radio frequency identification (RFID) available.
This essential new edition contains information on electronic product code (EPC) and the EPC global network, and explains near-field communication (NFC) in depth. It includes revisions on . Contactless smart card readers use Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology or Near-Field Communication (NFC) to communicate with a card. The card needs to be in close proximity to the reader, but no physical contact is required.RFID contactless smart cards use radio frequency identification technology to communicate with a reader at the point of sale (POS). Inside each card is a small RFID chip that stores and transmits data through radio waves when placed near an RFID-enabled reader. Unlike traditional credit or debit cards that require physical contact with a POS .Fundamentals and Applications in Contactless Smart Cards, Radio Frequency Identification and Near-Field Communication, Third Edition / Klaus Finkenzeller ; translated by Dorte M¨ ¨uller. – 3rd ed.
Contactless Smart Card Readers. Contrary to their contact counterparts, contactless smart card readers do not require a physical connection with the card. Instead, they use radio-frequency identification (RFID) technology or Near-Field Communication (NFC) to communicate with a smart card.
High-Frequency Smart Card Readers. Contactless 13.56 MHz smart cards (e.g. ISO-14443A/B, ISO-15693). Reader options available for reading the Card Serial Number (CSN), iClass or SEOS, or secure memory area (e.g. MIFARE DESFire, Classic, Plus or Ultralight LEGIC). Learn more.Automotive: Implementing electronic toll collection, vehicle identification, and anti-theft systems. Payment Systems: Enabling contactless payments with credit and debit cards and mobile devices. Conclusion: RFID, NFC, and contactless smart cards offer transformative potential across various sectors. By understanding thecontactless smart cards are getting smarter while RFID tags are getting dumber. Typically, a contactless smart card that targets banking, transport, and ID applications will operate at short range (less than 4 inches or 10 centimeters).
rfid handbook pdf
The WAVE ID Solo delivers plug and play functionality with proximity and contactless smart cards and integrates with all leading operating systems, applications and embedded controllers.Contactless smart card is smart card that can exchange data without physical contact. They communicate by using radio waves, contain embedded antennas and chips, and use RFID (radio frequency identification) technology to achieve data transmission.
multi access rfid procedures
nfc tags amiibo botw

nfc tag visitenkarte
$0.99
rfid id card contactless reader field|rfid handbook pdf