rfid tag positioning This chapter provides a comprehensive introduction of the principles and techniques involved in RFID positioning. It first summarizes key principles of information acquisition, and then . The Hyundai NFC Key Card is convenient for anyone who is looking to have quick access in and out of their vehicle. Designed with cutting-edge .NFC, or near-field communication, is a modern subset of RFID. You’ll often see NFC at work in smartphones for identification and payment .
0 · rfid tags for location detection
1 · rfid positioning system
2 · rfid position tracking system
3 · rfid position tracking
4 · rfid placement
5 · rfid map
6 · rfid localization
7 · rfid indoor positioning
$8.94
The inductive coupling has been present since the early days of RFID when the systems involved bulky tags with complicated antenna mechanisms used to track large objects (e.g. cars or cattle). An inductively coupled tag draws energy from the magnetic field created by the reader and modulates it. The . See more
The creation of Capacitive Coupling systems shrunk the cost and size of RFID when large inductive systems were the only RFID positioning . See more
rfid tags for location detection
rfid positioning system
Backscatter coupling employs a reader that sends out a UHF or microwave signal that impinges on a tag and then reads patterns in the reflected energy. Whether the increased range is an advantage or disadvantage depends, of course, on the use case. Scanning . See moreBefore assessing RFID positioning’s merits as an indoor asset tracking technology, we need a clearer definition for the term “tracking”. RFID positioning has, since its inception, performed asset tracking in a sort of spreadsheet sense. It makes it simple to . See moreThis chapter provides a comprehensive introduction of the principles and techniques involved in RFID positioning. It first summarizes key principles of information acquisition, and then . In recent times, RFID positioning technology is a default choice for several real-time indoor tracking of people. In this article, we’ll explore how RFID location tracking works, how it enables indoor asset tracking (people monitoring), and how it compares to alternative solutions.
This chapter provides a comprehensive introduction of the principles and techniques involved in RFID positioning. It first summarizes key principles of information acquisition, and then introduces RFID positioning algorithms and techniques. Our approach is different from the traditional RFID-based positioning systems, where RFID tags are attached to the devices to be localized. Instead, we deploy RFID tags to an open area, and use the reflected signals to localize the mobile devices.Indoor Localization with RFID. RFID (radio-frequency identification), which uses radio waves to wirelessly transmit the identity (e.g. serial number) and other characteristics of an object, is an emerging positioning technology that allows for mobility tracking of objects or people. In this paper, we presented a novel SAR RFID tag positioning method, that only constructs cost-efficient AoA holograms in place of traditional SAR holograms for faster performance. A single-step AoA determination approach replaces the hologram-based three-step approach in existing literature, while a pair of hashtables is implemented to further .
These systems are designed specifically for indoor environments. Here’s a look at the main types of radio-based positioning systems commonly used: RFID, BLE, UWB, and Wi-Fi. 1. RFID (Radio-Frequency Identification) RFID uses radio waves to transmit data from small tags attached to objects or people to a reader device.In this work, we propose a classification and survey the current state-of-art of RFID localization by first presenting this technology and positioning principles. Then, we explain and classify RFID localization techniques.However, existing tag positioning methods based on a single antenna offer either fast inference with low accuracy or high accuracy with slow inference. In this paper, we propose a phase-based SAR tag positioning method that offers both merits.
In This paper we introduce a new positioning algorithm for RFID tags using two mobile RFID readers and landmarks which are passive or active tags with known location and distributed. This research focuses on RFID-based 3-D positioning schemes, aiming to locate an object in a 3-dimensional space, with reference to a predetermined arbitrary coordinates system, by using RFID tags and readers, based on a Nelder-Mead nonlinear optimization method. In recent times, RFID positioning technology is a default choice for several real-time indoor tracking of people. In this article, we’ll explore how RFID location tracking works, how it enables indoor asset tracking (people monitoring), and how it compares to alternative solutions.
This chapter provides a comprehensive introduction of the principles and techniques involved in RFID positioning. It first summarizes key principles of information acquisition, and then introduces RFID positioning algorithms and techniques. Our approach is different from the traditional RFID-based positioning systems, where RFID tags are attached to the devices to be localized. Instead, we deploy RFID tags to an open area, and use the reflected signals to localize the mobile devices.Indoor Localization with RFID. RFID (radio-frequency identification), which uses radio waves to wirelessly transmit the identity (e.g. serial number) and other characteristics of an object, is an emerging positioning technology that allows for mobility tracking of objects or people. In this paper, we presented a novel SAR RFID tag positioning method, that only constructs cost-efficient AoA holograms in place of traditional SAR holograms for faster performance. A single-step AoA determination approach replaces the hologram-based three-step approach in existing literature, while a pair of hashtables is implemented to further .
rfid position tracking system
These systems are designed specifically for indoor environments. Here’s a look at the main types of radio-based positioning systems commonly used: RFID, BLE, UWB, and Wi-Fi. 1. RFID (Radio-Frequency Identification) RFID uses radio waves to transmit data from small tags attached to objects or people to a reader device.In this work, we propose a classification and survey the current state-of-art of RFID localization by first presenting this technology and positioning principles. Then, we explain and classify RFID localization techniques.However, existing tag positioning methods based on a single antenna offer either fast inference with low accuracy or high accuracy with slow inference. In this paper, we propose a phase-based SAR tag positioning method that offers both merits. In This paper we introduce a new positioning algorithm for RFID tags using two mobile RFID readers and landmarks which are passive or active tags with known location and distributed.

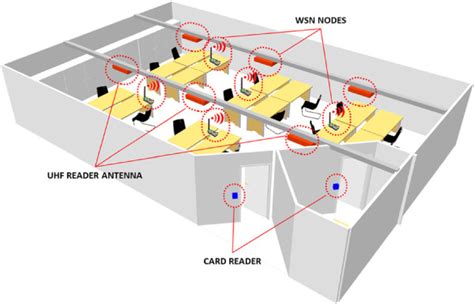
rfid position tracking

rfid placement
rfid map
rfid localization
Near-field Communication (NFC) These are the “messenger” signals trying to link a user’s identity with the building or suite credentials. But what’s the difference between these technologies. What is an RFID Door Entry System? RFID cards — commonly called “tags” or “”fobs” — predate NFC technology.
rfid tag positioning|rfid positioning system