smart card linux One of the authentication methods supported by the SSH protocol is public . Power up the Nintendo NFC Reader/Writer and make sure that the system and the .
0 · write certificate to smart card
1 · ubuntu smart card
2 · smart card based authentication
3 · smart card authentication step by
4 · smart card authentication
5 · read certificate from smart card
6 · linux smart card authentication
7 · 4.5.12 configure smart card authentication
This is an Explorer Application for working with MIFARE Ultralight C NFC tags. .
To enable smart card authentication we should rely on a module that allows PAM supported systems to use X.509 certificates to authenticate logins. The module relies on a PKCS#11 .
Overview. In this guide you’ll learn how to configure Smart Card authentication .
write certificate to smart card
ubuntu smart card
The owner must physically have the smart card, and they must know the PIN to .One of the authentication methods supported by the SSH protocol is public .By carefully selecting the right combination of smart cards and card readers, a fully functional system can be implemented with Debian. There are two main types of solution on Debian, the .To enable smart card authentication we should rely on a module that allows PAM supported systems to use X.509 certificates to authenticate logins. The module relies on a PKCS#11 library, such as opensc-pkcs11 to access the smart card for the credentials it will need.
This page explains how to setup your system in order to use a smart card reader.By carefully selecting the right combination of smart cards and card readers, a fully functional system can be implemented with Debian. There are two main types of solution on Debian, the OpenPGP based cards or the PKCS#11 style cards. This .This section describes what a smart card is and how smart card authentication works. It describes the tools that you can use to read and manipulate smart card content.Overview. In this guide you’ll learn how to configure Smart Card authentication using SSSD as authentication daemon in a way that can be used both for user interface access via GDM login and unlock and also some basic principles that are common to headless setups.
Here we learned how to set up smart card authentication in Linux. It involves an AD eco-system, a physical smart card to store your keys and certificate, card reader (and drivers if applicable). On a usual Linux node, the OS will communicate with card via PC/SC protocol and low-level CCID driver.The owner must physically have the smart card, and they must know the PIN to unlock it. This provides a higher degree of security than single-factor authentication (such as just using a password). In this page, we describe how to enable smart card authentication on Ubuntu. .To configure smart card authentication centrally, use the enhanced smart card functionality provided by the System Security Services Daemon (SSSD). For details, see Smart-card Authentication in Identity Management in the Linux Domain .
In Red Hat Enterprise Linux, we strive to support several popular smart-card types. However, because it is not possible to support every smart card available, this document specifies our targeted cards. In addition it provides information on how to investigate a potential incompatibility between the cards and RHEL.One of the authentication methods supported by the SSH protocol is public key authentication. A public key is copied to the SSH server where it is stored and marked as authorized. The owner of the corresponding private key in the smart card can then SSH login to the server.To enable smart card authentication we should rely on a module that allows PAM supported systems to use X.509 certificates to authenticate logins. The module relies on a PKCS#11 library, such as opensc-pkcs11 to access the smart card for the credentials it will need.
This page explains how to setup your system in order to use a smart card reader.By carefully selecting the right combination of smart cards and card readers, a fully functional system can be implemented with Debian. There are two main types of solution on Debian, the OpenPGP based cards or the PKCS#11 style cards. This .This section describes what a smart card is and how smart card authentication works. It describes the tools that you can use to read and manipulate smart card content.Overview. In this guide you’ll learn how to configure Smart Card authentication using SSSD as authentication daemon in a way that can be used both for user interface access via GDM login and unlock and also some basic principles that are common to headless setups.
smart card based authentication
Here we learned how to set up smart card authentication in Linux. It involves an AD eco-system, a physical smart card to store your keys and certificate, card reader (and drivers if applicable). On a usual Linux node, the OS will communicate with card via PC/SC protocol and low-level CCID driver.The owner must physically have the smart card, and they must know the PIN to unlock it. This provides a higher degree of security than single-factor authentication (such as just using a password). In this page, we describe how to enable smart card authentication on Ubuntu. .To configure smart card authentication centrally, use the enhanced smart card functionality provided by the System Security Services Daemon (SSSD). For details, see Smart-card Authentication in Identity Management in the Linux Domain .In Red Hat Enterprise Linux, we strive to support several popular smart-card types. However, because it is not possible to support every smart card available, this document specifies our targeted cards. In addition it provides information on how to investigate a potential incompatibility between the cards and RHEL.


smart card authentication step by
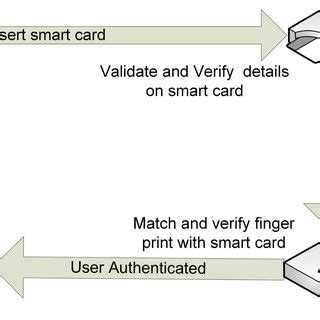
smart card authentication
read certificate from smart card
linux smart card authentication
OLED Switch Lite display kits to go on sale September 26th. The little brother .
smart card linux|smart card authentication