linux smart card driver The following packages must be installed to obtain a smart card configuration on Ubuntu: pcscd: contains the drivers needed to communicate with the CCID smart card readers. opensc . Manage your adult Oyster and contactless cards on the move with the app. • Top up pay as you go credit. • Buy adult rate 7 Day, Monthly and Annual .
0 · write certificate to smart card
1 · ubuntu smart card
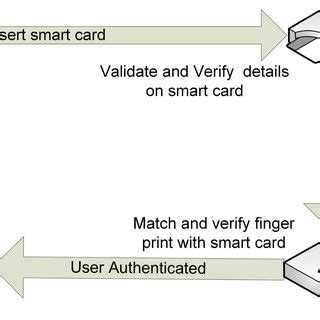
2 · smart card based authentication
3 · smart card authentication step by
4 · smart card authentication
5 · read certificate from smart card
6 · linux smart card authentication
7 · 4.5.12 configure smart card authentication
We provide NFC products of all kinds, worldwide, every day. Launched in 2012, Shop NFC is now a landmark in Near Field Communication technology. We rapidly deliver NFC Tags, Smart Cards, NFC Readers and Accessories of any .
The following packages must be installed to obtain a smart card configuration on Ubuntu: pcscd: contains the drivers needed to communicate with the CCID smart card readers. opensc .

Overview. In this guide you’ll learn how to configure Smart Card authentication .There used to be a driver for PC/SC that supported this card reader: pcsc-lite-cm2020, however, it seems to be gone now. I've downloaded the source package from the manufacturer. It is very old.This page explains how to setup your system in order to use a smart card reader. Installation. Install pcsclite and ccid. Note: The package ccid provides a generic USB interface driver for .Install OpenSC. For Mac OS X, download and install SCA. For Windows, visit the build project. For Linux, either use your distribution's package manager or see Compiling and Installing on Unix flavors. Test OpenSC. First check if your smart card reader is found: $ opensc-tool --list-readers. Readers known about: Nr. Driver Name.
Some vendors provide binary (closed source) drivers for Linux, but it is not always necessary to use these drivers. In the best cases, it is possible to build working solutions without using any . Here we learned how to set up smart card authentication in Linux. It involves an AD eco-system, a physical smart card to store your keys and certificate, card reader (and .
Overview. In this guide you’ll learn how to configure Smart Card authentication using SSSD as authentication daemon in a way that can be used both for user interface access via GDM login .Chapter 1. Understanding smart card authentication. Copy link. Authentication based on smart cards is an alternative to passwords. You can store user credentials on a smart card in the .
We will use opensc-pkcs11 on the client to access the smart card drivers, and we will copy the public key from the smart card to the SSH server to make the authentication work. The .
The following packages must be installed to obtain a smart card configuration on Ubuntu: pcscd: contains the drivers needed to communicate with the CCID smart card readers. opensc-pkcs11: (optional, depending on your smartcard hardware) contains the smart card drivers, such as Personal Identify Verification (PIV) or Common Access Card (CAC)There used to be a driver for PC/SC that supported this card reader: pcsc-lite-cm2020, however, it seems to be gone now. I've downloaded the source package from the manufacturer. It is very old.RHEL 7 was originally shipped with CoolKey smart cards driver, which was deprecated and is no longer available in RHEL 8 and newer. The current driver OpenSC supports all cards that used to be supported by CoolKey.
This page explains how to setup your system in order to use a smart card reader. Installation. Install pcsclite and ccid. Note: The package ccid provides a generic USB interface driver for smart card reader.Some vendors provide binary (closed source) drivers for Linux, but it is not always necessary to use these drivers. In the best cases, it is possible to build working solutions without using any non-free or binary artifacts from the vendor, except for those in the card itself.Overview. In this guide you’ll learn how to configure Smart Card authentication using SSSD as authentication daemon in a way that can be used both for user interface access via GDM login and unlock and also some basic principles that are common to headless setups. Here we learned how to set up smart card authentication in Linux. It involves an AD eco-system, a physical smart card to store your keys and certificate, card reader (and drivers if applicable). On a usual Linux node, the OS will communicate with card via PC/SC protocol and low-level CCID driver.
Chapter 1. Understanding smart card authentication. Copy link. Authentication based on smart cards is an alternative to passwords. You can store user credentials on a smart card in the form of a private key and a certificate, and special software and hardware is used to access them.The following packages must be installed to obtain a smart card configuration on Ubuntu: pcscd: contains the drivers needed to communicate with the CCID smart card readers. opensc-pkcs11: (optional, depending on your smartcard hardware) contains the smart card drivers, such as Personal Identify Verification (PIV) or Common Access Card (CAC)Follow this procedure to perform the following tasks: Generate the OpenSSL certificate authority. Create a certificate signing request. Warning. The following steps are intended for testing purposes only.The following packages must be installed to obtain a smart card configuration on Ubuntu: pcscd: contains the drivers needed to communicate with the CCID smart card readers. opensc-pkcs11: (optional, depending on your smartcard hardware) contains the smart card drivers, such as Personal Identify Verification (PIV) or Common Access Card (CAC)
There used to be a driver for PC/SC that supported this card reader: pcsc-lite-cm2020, however, it seems to be gone now. I've downloaded the source package from the manufacturer. It is very old.RHEL 7 was originally shipped with CoolKey smart cards driver, which was deprecated and is no longer available in RHEL 8 and newer. The current driver OpenSC supports all cards that used to be supported by CoolKey.
This page explains how to setup your system in order to use a smart card reader. Installation. Install pcsclite and ccid. Note: The package ccid provides a generic USB interface driver for smart card reader.Some vendors provide binary (closed source) drivers for Linux, but it is not always necessary to use these drivers. In the best cases, it is possible to build working solutions without using any non-free or binary artifacts from the vendor, except for those in the card itself.Overview. In this guide you’ll learn how to configure Smart Card authentication using SSSD as authentication daemon in a way that can be used both for user interface access via GDM login and unlock and also some basic principles that are common to headless setups. Here we learned how to set up smart card authentication in Linux. It involves an AD eco-system, a physical smart card to store your keys and certificate, card reader (and drivers if applicable). On a usual Linux node, the OS will communicate with card via PC/SC protocol and low-level CCID driver.

Chapter 1. Understanding smart card authentication. Copy link. Authentication based on smart cards is an alternative to passwords. You can store user credentials on a smart card in the form of a private key and a certificate, and special software and hardware is used to access them.
write certificate to smart card
The following packages must be installed to obtain a smart card configuration on Ubuntu: pcscd: contains the drivers needed to communicate with the CCID smart card readers. opensc-pkcs11: (optional, depending on your smartcard hardware) contains the smart card drivers, such as Personal Identify Verification (PIV) or Common Access Card (CAC)
what powers rfid chip

1. Reply. N_T_F_D • 2 mo. ago. You can soak the card in acetone to remove the plastic and keep the chip and antenna, so it's possible to do it but you need to be extremely .
linux smart card driver|read certificate from smart card