rfid implant how does it work the intrapnent system The RFID implant, also known as a biochip or microchip implant, is a small electronic device that is inserted under the skin. It contains an RFID chip and antenna that . $58.99
0 · rfid microchip implant
1 · microchip implants wiki
2 · microchip implant failure
3 · how to get rfid implanted
4 · first rfid implant
5 · benefits of a rfid implant
6 · are rfid implants safe
The ACR122U NFC Reader is a PC-linked contactless smart card reader/writer developed .Retrieved 16 February 2017. ^ Galaxy S IV Mini (Variant) SCH-I435, Samsung, 14 June 2014. ^ Galaxy S IV Mini (Variant) SM-S890L (PDF), Samsung, 14 June 2014. ^ Turkcell T40 Aygün, Turkcell. ^ Vodafone Smart III, Vodafone, archived from the original on 30 June 2013, retrieved 27 June 2013. ^ "NXP . See more
Key Takeaways. Theoretically, RFID implants offer practical benefits as contactless payments, unlocking doors, and accessing medical data, with just a wave of your hand. However, the implants still face challenges such as safety concerns, potential infections, and limited data .RFID implants communicate with nearby scanning devices via radio waves. When the scanning device is close to the implant, the chip inside the implant transmits a unique ID number or .
The RFID implant, also known as a biochip or microchip implant, is a small electronic device that is inserted under the skin. It contains an RFID chip and antenna that .A human microchip implant is any electronic device implanted subcutaneously (subdermally) usually via an injection. Examples include an identifying integrated circuit RFID device encased in silicate glass which is implanted in the body of a human being. This type of subdermal implant usually contains a unique ID number that can be linked to information contained in an external database, such as identity document, criminal record, medical history, medications, address book, . Here, we explain implanted RFID technology, its potential uses, and what is and is not known about its safety. We present images of a patient with an RFID chip who presented .RFID (radio frequency identification) chips are microelectronic devices that store data. RFID chips implanted in the human body are usually passive chips, meaning they do not require an .
rfid microchip implant
Sure, the technology—a millimeters-long microchip equipped with near-field communication capabilities and lodged just under the skin—had a niche, cutting-edge appeal, .Key Takeaways. Theoretically, RFID implants offer practical benefits as contactless payments, unlocking doors, and accessing medical data, with just a wave of your hand. However, the implants still face challenges such as safety concerns, potential .RFID implants communicate with nearby scanning devices via radio waves. When the scanning device is close to the implant, the chip inside the implant transmits a unique ID number or other data, which the scanning device receives and can then perform the corresponding action, such as unlocking a door, completing a payment, or accessing data.
The RFID implant, also known as a biochip or microchip implant, is a small electronic device that is inserted under the skin. It contains an RFID chip and antenna that allow it to communicate wirelessly with RFID readers.A human microchip implant is any electronic device implanted subcutaneously (subdermally) usually via an injection. Examples include an identifying integrated circuit RFID device encased in silicate glass which is implanted in the body of a human being. Here, we explain implanted RFID technology, its potential uses, and what is and is not known about its safety. We present images of a patient with an RFID chip who presented to our clinic for acute metacarpal and phalangeal fractures, to demonstrate the clinical and radiographic appearance of these chips.RFID (radio frequency identification) chips are microelectronic devices that store data. RFID chips implanted in the human body are usually passive chips, meaning they do not require an internal power supply but instead generate electricity through received radio waves to send data.
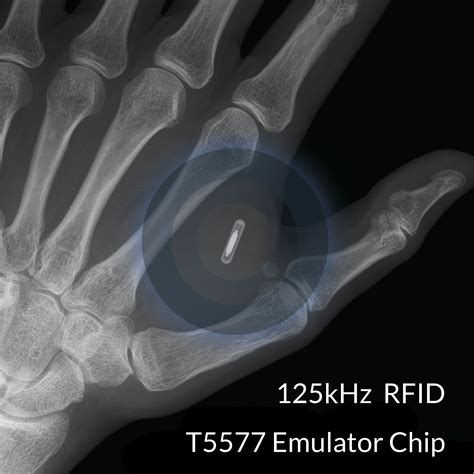
Sure, the technology—a millimeters-long microchip equipped with near-field communication capabilities and lodged just under the skin—had a niche, cutting-edge appeal, but in practical terms, a fob. RFID Implants are simple, cheap, and battery-free. While embedding RFID tags under the skin delivers us this world of contactless payments, magic locks, and the ability to be tracked. Other payment implants are based on radio-frequency identification (RFID), which is the similar technology typically found in physical contactless debit and credit cards. Walletmor. An x-ray.
Radio frequency identification (RFID) implants are an emerging technology that can make everyday life easier. They’re capable of storing information, making payments, replacing keys, and.Key Takeaways. Theoretically, RFID implants offer practical benefits as contactless payments, unlocking doors, and accessing medical data, with just a wave of your hand. However, the implants still face challenges such as safety concerns, potential .
RFID implants communicate with nearby scanning devices via radio waves. When the scanning device is close to the implant, the chip inside the implant transmits a unique ID number or other data, which the scanning device receives and can then perform the corresponding action, such as unlocking a door, completing a payment, or accessing data.
The RFID implant, also known as a biochip or microchip implant, is a small electronic device that is inserted under the skin. It contains an RFID chip and antenna that allow it to communicate wirelessly with RFID readers.A human microchip implant is any electronic device implanted subcutaneously (subdermally) usually via an injection. Examples include an identifying integrated circuit RFID device encased in silicate glass which is implanted in the body of a human being. Here, we explain implanted RFID technology, its potential uses, and what is and is not known about its safety. We present images of a patient with an RFID chip who presented to our clinic for acute metacarpal and phalangeal fractures, to demonstrate the clinical and radiographic appearance of these chips.
RFID (radio frequency identification) chips are microelectronic devices that store data. RFID chips implanted in the human body are usually passive chips, meaning they do not require an internal power supply but instead generate electricity through received radio waves to send data. Sure, the technology—a millimeters-long microchip equipped with near-field communication capabilities and lodged just under the skin—had a niche, cutting-edge appeal, but in practical terms, a fob. RFID Implants are simple, cheap, and battery-free. While embedding RFID tags under the skin delivers us this world of contactless payments, magic locks, and the ability to be tracked. Other payment implants are based on radio-frequency identification (RFID), which is the similar technology typically found in physical contactless debit and credit cards. Walletmor. An x-ray.
microchip implants wiki
microchip implant failure
how to get rfid implanted
blank smart card
$27.99
rfid implant how does it work the intrapnent system|microchip implants wiki