rfid chip 2019 RFID chips (wearable or implanted) would work best at electro-chemical biosensing of bodily functions like monitoring glucose or cholesterol levels as well as body temperature or heart function (care context) (Masters & Michael, 2007; Xiang et al., 2022, p. 7). It’s unlikley the tag stores any filament parameters, only a filament ID which printer checks the C-Code against. If the printer or the phone app could write to them, it would be a cool feature and product line for Bambu to sell .
0 · where are rfid chips used
1 · types of rfid chips
2 · rfid chips in humans
3 · rfid chips for sale
4 · rfid chip pros and cons
5 · rfid chip meaning
6 · rfid chip manufacturing
7 · pros and cons of rfid
RFID Reader Mini ID IC Card Reader Scanner RFID Reader 125KHz/13.56Mhz Dual .
RFID. R adio-frequency identification (RFID) technology has been in use for over 50 years. The technology involves a microchip attached to an antenna, which responds to an incoming signal from a reader by sending an outgoing signal. RFID chips (wearable or implanted) would work best at electro-chemical biosensing of bodily functions like monitoring glucose or cholesterol levels as well as body temperature or . RFID. R adio-frequency identification (RFID) technology has been in use for over 50 years. The technology involves a microchip attached to an antenna, which responds to an incoming signal from a reader by sending an outgoing signal.
RFID chips (wearable or implanted) would work best at electro-chemical biosensing of bodily functions like monitoring glucose or cholesterol levels as well as body temperature or heart function (care context) (Masters & Michael, 2007; Xiang et al., 2022, p. 7).
Other payment implants are based on radio-frequency identification (RFID), which is the similar technology typically found in physical contactless debit and credit cards. Microchip implants are going from tech-geek novelty to genuine health tool—and you might be running out of good reasons to say no. By Haley Weiss. Professor Kevin Warwick holds up an RFID .A human microchip implant is any electronic device implanted subcutaneously (subdermally) usually via an injection. Examples include an identifying integrated circuit RFID device encased in silicate glass which is implanted in the body of a human being.
This study will review how human RFID microchip implants will impact and effect security, privacy, and ethical concerns associated with the new initiative for RFID implants to be used on human beings in everyday activities. The benefits of an implantable RFID chip, which is durable and about the size of a grain of rice, can hold or link to information about the identity, physiological characteristics, health . An RFID chip is typically a simple piece of hardware with a unique identifier and a small amount of read/write storage. Currently, this storage is insufficient for significant medical information, so the chip usually stores only a patient identifier, which links to a complete electronic record stored separately.To address this storage-of-data limitation, the silicon RFID chip was developed. Auto ID-based technologies such as optical barcodes and RFID address the function of "contactless" behavior, which eliminates the impracticalities of mechanical touch and enables the performance of .
Radio frequency identification (RFID) has been considered one of the most promising technologies in healthcare and has been recognized as a smart tool with the potential to overcome many challenges that health care encounters such as inaccurate pharmaceutical stock, inability to track medical equipment, difficulty in tracking patient locations .
where are rfid chips used
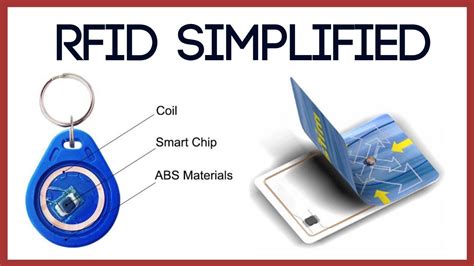
RFID. R adio-frequency identification (RFID) technology has been in use for over 50 years. The technology involves a microchip attached to an antenna, which responds to an incoming signal from a reader by sending an outgoing signal. RFID chips (wearable or implanted) would work best at electro-chemical biosensing of bodily functions like monitoring glucose or cholesterol levels as well as body temperature or heart function (care context) (Masters & Michael, 2007; Xiang et al., 2022, p. 7).
prolific games card smart axe
Other payment implants are based on radio-frequency identification (RFID), which is the similar technology typically found in physical contactless debit and credit cards. Microchip implants are going from tech-geek novelty to genuine health tool—and you might be running out of good reasons to say no. By Haley Weiss. Professor Kevin Warwick holds up an RFID .A human microchip implant is any electronic device implanted subcutaneously (subdermally) usually via an injection. Examples include an identifying integrated circuit RFID device encased in silicate glass which is implanted in the body of a human being.
This study will review how human RFID microchip implants will impact and effect security, privacy, and ethical concerns associated with the new initiative for RFID implants to be used on human beings in everyday activities. The benefits of an implantable RFID chip, which is durable and about the size of a grain of rice, can hold or link to information about the identity, physiological characteristics, health . An RFID chip is typically a simple piece of hardware with a unique identifier and a small amount of read/write storage. Currently, this storage is insufficient for significant medical information, so the chip usually stores only a patient identifier, which links to a complete electronic record stored separately.
types of rfid chips
To address this storage-of-data limitation, the silicon RFID chip was developed. Auto ID-based technologies such as optical barcodes and RFID address the function of "contactless" behavior, which eliminates the impracticalities of mechanical touch and enables the performance of .

rfid chips in humans

print driving license smart card
project fi sim card smart watch
ST25 NFC/RFID tags and readers. Near field communication (NFC) is a specialized subset of the 13.56 MHz RFID HF technology. NFC is a convenient, always-on, low-power wireless technology, which operates within a 10 cm .Information. NFC Tools GUI is a cross Platform software : it works on Mac, Windows and Linux. You can read and write your NFC chips with a simple and lightweight user interface. Connect your NFC reader to your computer like the .QUICK ANSWER. NFC tags and readers communicate wirelessly with each other over very short distances. Tags store a small amount of data .
rfid chip 2019|rfid chip pros and cons