smart card database The following functions manage the smart card database, updating the database . Ray/Hood Radio. 10-11AM. Davis Jones' Locker. 11AM-12PM. CHECKERS N CHIPS. 12-1PM. Boulevard of Folken Dreams. . Auburn, AL 36849 (334) 844-9345. Schedule; Connect; About Us; Read; Watch; Listen; FCC Public .
0 · what constitutes a smart card
1 · smart data sign in
2 · smart card information
3 · smart card identity
4 · smart card identification
5 · smart card based identification system
6 · smart card based authentication
7 · jpmorgan smart data sign in
985 Lincoln Way, Suite 103 Auburn, CA 95603. Telephone. (530) 885-5636. Email. [email protected]. Add this radio's widget to your website. Broadcast Monitoring by ACRCloud. .
The following functions query the smart card database. They can provide a list of .The following functions manage the smart card database, updating the database .The smart card resource manager manages access to readers and to smart cards. .Track smart cards within readers. Smart Card and Reader Access Functions. .
what constitutes a smart card
smart data sign in
The following functions manage the smart card database, updating the database . The smart card resource manager manages access to readers and to smart .
Smart card is today the most widespread secured portable computing device. Four years ago, we addressed the problem of scaling down .
The design of very small databases for smart cards and for portable embedded .
The following functions query the smart card database. They can provide a list of smart cards supplied by a specific user, the interfaces and primary service provider of a specific card, the reader groups defined for the system, and the readers within a set of reader groups. The following functions manage the smart card database, updating the database by using a specified resource manager context. The smart card resource manager manages access to readers and to smart cards. To manage these resources, it performs the following functions. Identifies and tracks resources. Allocates readers and resources across multiple applications. Supports transaction primitives for accessing services available on a given card.
Smart card is today the most widespread secured portable computing device. Four years ago, we addressed the problem of scaling down database techniques for the smart card and we proposed.
The design of very small databases for smart cards and for portable embedded systems is deeply constrained by the peculiar features of the physical medium. Privacy concerns are relevant due to the fact that personal information may . The smart card resource manager manages access to readers and to smart cards. To manage these resources, it performs the following functions. Identifies and tracks resources. Allocates readers and resources across multiple applications. Supports transaction primitives for accessing services available on a given card. [!Note]With an embedded microcontroller, smart cards have the unique ability to store large amounts of data, carry out their own on-card functions (e.g., encryption and mutual authentication) and interact intelligently with a smart card reader. The steps would generally be: user logs into computer using CAC, open the Access database, navigate to the check-in form, insert the new-join's card into the second card reader, somehow get data from the card, auto-fill the form with the fresh data, and finish doing whatever I make it do.
Track smart cards within readers. Smart Card and Reader Access Functions. Connect to and communicate with a smart card, including transferring data using T=0, T=1, and raw protocols. Direct Card Access Functions. Communicate with cards that may not conform to the ISO 7816 specifications.mart Card Identification Management over a Distributed Database Model. Instead of having multiple identity cards like driving licenses, work permits, employee cards, passports, voters cards, a single national identity card with in-built smart features including biometrics and advanced identification features that . The following functions query the smart card database. They can provide a list of smart cards supplied by a specific user, the interfaces and primary service provider of a specific card, the reader groups defined for the system, and the readers within a set of reader groups.
smart card information
The following functions manage the smart card database, updating the database by using a specified resource manager context.
The smart card resource manager manages access to readers and to smart cards. To manage these resources, it performs the following functions. Identifies and tracks resources. Allocates readers and resources across multiple applications. Supports transaction primitives for accessing services available on a given card. Smart card is today the most widespread secured portable computing device. Four years ago, we addressed the problem of scaling down database techniques for the smart card and we proposed.
The design of very small databases for smart cards and for portable embedded systems is deeply constrained by the peculiar features of the physical medium. Privacy concerns are relevant due to the fact that personal information may .
The smart card resource manager manages access to readers and to smart cards. To manage these resources, it performs the following functions. Identifies and tracks resources. Allocates readers and resources across multiple applications. Supports transaction primitives for accessing services available on a given card. [!Note]With an embedded microcontroller, smart cards have the unique ability to store large amounts of data, carry out their own on-card functions (e.g., encryption and mutual authentication) and interact intelligently with a smart card reader. The steps would generally be: user logs into computer using CAC, open the Access database, navigate to the check-in form, insert the new-join's card into the second card reader, somehow get data from the card, auto-fill the form with the fresh data, and finish doing whatever I make it do. Track smart cards within readers. Smart Card and Reader Access Functions. Connect to and communicate with a smart card, including transferring data using T=0, T=1, and raw protocols. Direct Card Access Functions. Communicate with cards that may not conform to the ISO 7816 specifications.
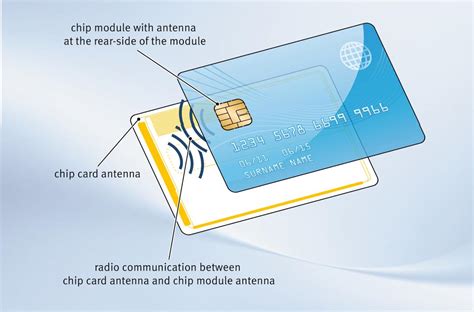
NFC tags are passive, meaning they don't have any power source. Instead, they literally draw power from the device that reads them, thanks to magnetic induction. When a reader gets close enough to a tag, it energizes it and .
smart card database|what constitutes a smart card