smart card protocol t0 t1 I have just discovered the reader that expects T0 communication even if the card ATR returns T1. Q: What is the logic must be to determine what protocol to use? And if there is a spec behind it, can you please point me out to it. As one of the pioneers of the RFID and NFC technology, ST offers a comprehensive range of HF RFID/NFC products, covering all the requirements for NFC-based applications. Designers can leverage ST’s extensive ecosystem to .
0 · The DS8007 and Smart Card Interface Fundamentals
1 · Smart cards – basic principles
2 · Smart card application protocol data unit
3 · Smart Card Reader T0 T1 communication on APDU level
4 · Smart Card Operation Using Freescale Microcontrollers
5 · ISO 7816
6 · 35.6.3.6 ISO 7816 for Smart Card Interfacing
Simple Radio, our free iOS and Android app. Continue listening to your favorite stations anytime, anywhere. KAHI Radio - KAHI, The Voice of the Foothills, AM 950, Auburn, CA. Live stream .
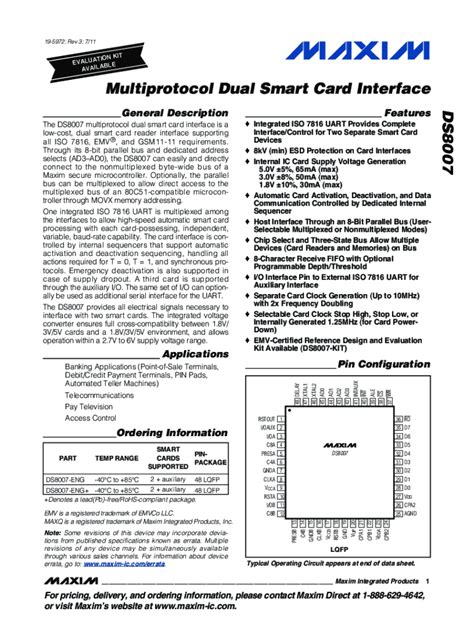
I have just discovered the reader that expects T0 communication even if the card ATR returns T1. Q: What is the logic must be to determine what protocol to use? And if there is a spec behind it, can you please point me out to it.The ISO 7816 standard defines the necessary protocols to communicate with a smart card. . The DS8007 provides all electrical signals necessary to physically interface a .
The SERCOM USART features an ISO/IEC 7816-compatible operating mode. This mode . In the context of smart cards, an application protocol data unit (APDU) is the .The T = 0 protocol is the predominant protocol in France and was the only protocol specified in .I have just discovered the reader that expects T0 communication even if the card ATR returns T1. Q: What is the logic must be to determine what protocol to use? And if there is a spec behind it, can you please point me out to it.
The ISO 7816 standard defines the necessary protocols to communicate with a smart card. Although the communication software is tested with TimeCOS, the basic communication protocol (ISO 7816, T = 0) implemented in this application note is common with all smart cards. 2012 Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
The DS8007 and Smart Card Interface Fundamentals
The DS8007 provides all electrical signals necessary to physically interface a microcontroller with two separate smart cards. The device contains a dedicated internal sequencer that controls automatic card activation and . T=0 is a byte based protocol while T=1 uses frames underneath. Most cards with T=0 don't support extended length. Note that to get extended length functionality that the javacardx.apdu.ExtendedLength tagging interface needs to be implemented. JCOP cards can be configured to use T=0/T=1/T=CL and others.The SERCOM USART features an ISO/IEC 7816-compatible operating mode. This mode permits interfacing with smart cards and Security Access Modules (SAM) communicating through an ISO 7816 link. Both T=0 and T=1 protocols defined by the ISO 7816 specification are supported.In the context of smart cards, an application protocol data unit (APDU) is the communication unit between a smart card reader and a smart card. The structure of the APDU is defined by ISO/IEC 7816 -4 Organization, security and commands for interchange .
The T = 0 protocol is the predominant protocol in France and was the only protocol specified in ISO 7816 - 3. In 1992 ISO standardised the T = 1 protocol as amendment 1 to ISO 7816 - 3. Clearly the IC card and the interface device must operate with a common protocol.
Smart cards – basic principles
ISO7816-3 specifies communication protocol between smart card and reader on the level of the electrical signals. • Protocol T=0 – byte-oriented protocol. Older than T1, designed for maximal simplicity and minimal memory requirements. Error detection only .Protocol T0/T1. There are two standardised data exchange protocols defined in ISO/IEC 7816-3 for the communication between a Smart Card and a terminal: the byte-oriented half duplex transmission protocol T=0 and the block-oriented half duplex protocol T=1.
If the card is able to process more than one protocol type and if one of those protocol types is indicated as T=0, then the protocol type T=0 shall indicated in TD1 as the first offered protocol, and is assumed if no PTS is performed.
I have just discovered the reader that expects T0 communication even if the card ATR returns T1. Q: What is the logic must be to determine what protocol to use? And if there is a spec behind it, can you please point me out to it.The ISO 7816 standard defines the necessary protocols to communicate with a smart card. Although the communication software is tested with TimeCOS, the basic communication protocol (ISO 7816, T = 0) implemented in this application note is common with all smart cards. 2012 Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
The DS8007 provides all electrical signals necessary to physically interface a microcontroller with two separate smart cards. The device contains a dedicated internal sequencer that controls automatic card activation and . T=0 is a byte based protocol while T=1 uses frames underneath. Most cards with T=0 don't support extended length. Note that to get extended length functionality that the javacardx.apdu.ExtendedLength tagging interface needs to be implemented. JCOP cards can be configured to use T=0/T=1/T=CL and others.The SERCOM USART features an ISO/IEC 7816-compatible operating mode. This mode permits interfacing with smart cards and Security Access Modules (SAM) communicating through an ISO 7816 link. Both T=0 and T=1 protocols defined by the ISO 7816 specification are supported.
what is smart shopper debit card
In the context of smart cards, an application protocol data unit (APDU) is the communication unit between a smart card reader and a smart card. The structure of the APDU is defined by ISO/IEC 7816 -4 Organization, security and commands for interchange .The T = 0 protocol is the predominant protocol in France and was the only protocol specified in ISO 7816 - 3. In 1992 ISO standardised the T = 1 protocol as amendment 1 to ISO 7816 - 3. Clearly the IC card and the interface device must operate with a common protocol.
ISO7816-3 specifies communication protocol between smart card and reader on the level of the electrical signals. • Protocol T=0 – byte-oriented protocol. Older than T1, designed for maximal simplicity and minimal memory requirements. Error detection only .Protocol T0/T1. There are two standardised data exchange protocols defined in ISO/IEC 7816-3 for the communication between a Smart Card and a terminal: the byte-oriented half duplex transmission protocol T=0 and the block-oriented half duplex protocol T=1.
what is smart card in hindi language

Smart card application protocol data unit
Where is the NFC reader in my phone? iPhone: The NFC reader is at the top of the back of your phone. Android: The NFC reader is either at the top or in the middle of the back of your phone. Other device: Search the web to confirm the .
smart card protocol t0 t1|Smart Card Reader T0 T1 communication on APDU level